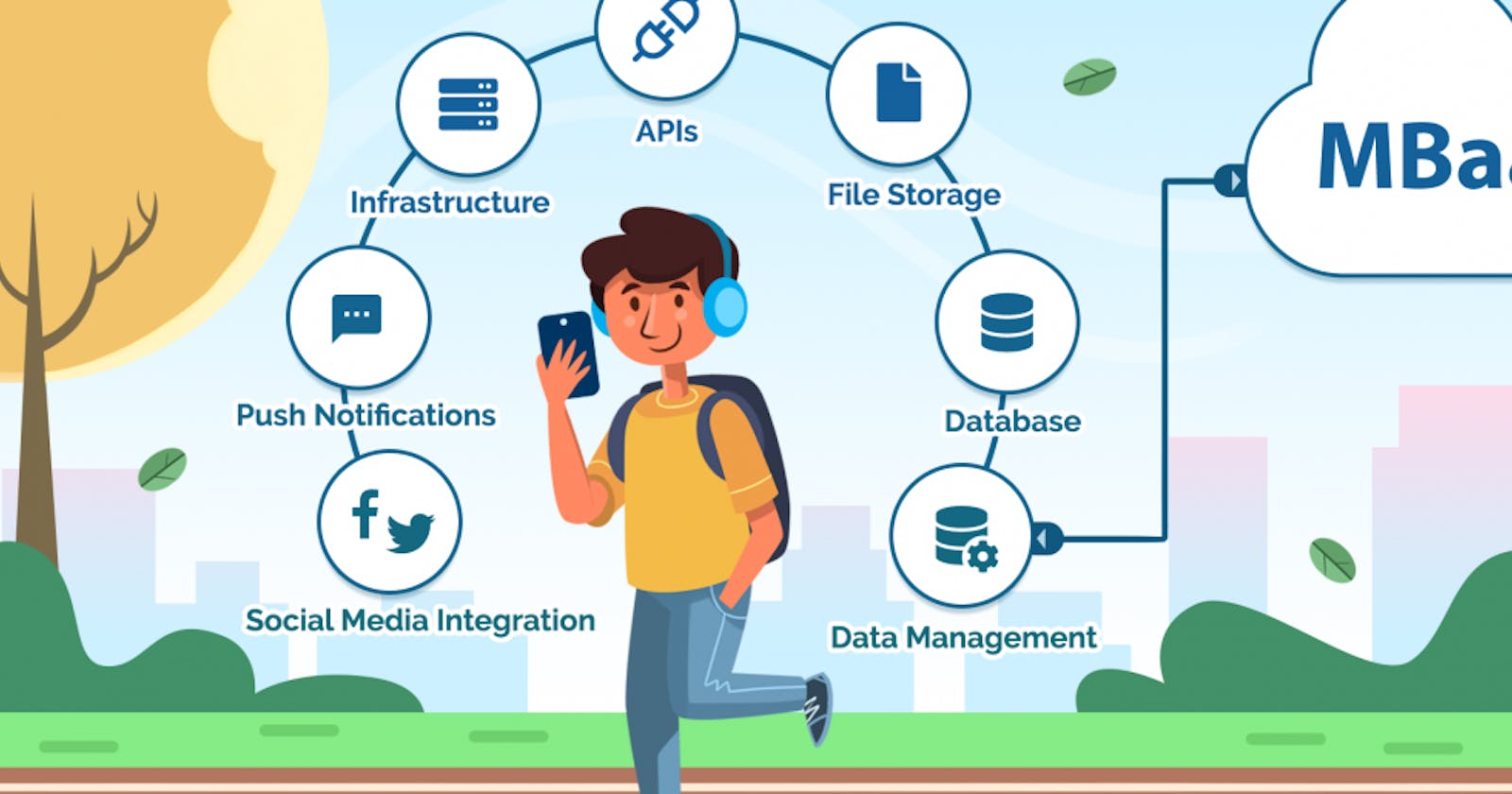
What is Backend as a Service (BaaS)?
A BaaS or mBaaS or Backend as a Service is a platform that automates backend side development and takes care of the cloud infrastructure. Using a BaaS, you will outsource the responsibilities of running and maintaining servers to a third party and focus on the frontend or client-side development. On top of that, a BaaS will provide a set of tools to help you to create a backend code and speed up the development process. It has ready to use features such as data management, APIs, social media integrations, file storage, and push notifications.
You can read the original article here:
Here is what you will learn reading this article:
- What is a Backend as a Service
- Frontend vs. Backend
- The differences between a BaaS vs. a Custom Backend
- BaaS vs. MBaaS
- The reasons to use a backend as a service
- When to use a BaaS
- Advantages and Disadvantages of a backend as a service
- BaaS versus infrastructure providers
- Main features of a backend as a service
- Who should use a BaaS
- How the architecture of a BaaS looks like
- Comparison of BaaS service providers
Frontend vs. Backend
First things, first! Here is a simple explanation of the differences between the frontend and backend. Every software application has a section that the user sees that is called the frontend. There is also a part that the user does not see that is named backend. These two portions combine through APIs.
Backend x Frontend
The following examples will help you to understand the differences between custom coding and using a BaaS.
Example 01 — BaaS x AWS EC2 Instances
Imagine you would like to build a new software project and that you will not use a BaaS. The first step to start developing a backend is to set up the servers. Here is how it will work:
- Login on AWS or any other cloud.
- Go to Instances
- Launch Instance
- Select the Operating System
- Instance Size, Type
- Configure Instance Details
- Number of instances
- Network
- IP
- Monitoring
- Other settings like Auto Scaling, IAM, etc
- Add Storage
- Security Settings
All right, your instance is up and running, and now you can start coding! Not really! This is only the first step of the process, and you will still need to install the webserver, database, framework, etc. After all that is done, you can start coding. The time to perform this process can range from a few hours (for a small project with skilled backend developers) to more than a day for large environments.
This same process using a backend as a service will be done with a few clicks and take no more than a few minutes.
Example 02 — BaaS x Custom coding Login feature
Imagine that after your server setup is ready and you want to develop the first feature of your application. Let’s consider the first feature you will code is a social login to Facebook. I will assume that the development will be outsourced to an offshore company and that will cost $25/hour. This simple task will take around 16 hours and cost $400.
On the other hand, using a BaaS will allow you to implement the same feature in less than one hour. You will have a saving of 15 hours and $375. Not bad for a simple task implementation!
Example 03 — GDPR security settings
GDPR privacy requirements are pretty complex, and the implementation will demand a lot of engineering effort. The requirements will range from implementing HTTPS for transit data to encrypt server-side data in rest (and several other conditions). The exact amount of engineering hours to fulfill all the elements will depend on the size and complexity of the project, but can easily surpass 100 hours of implementation.
Outsourcing this implementation to the backend as a service company makes a lot of sense in special for small to medium projects. I say that because the backend platforms can dilute the investment made to implement GDPR settings among hundreds or thousands of apps, and the stake per app will be minimal. A company with a single project will have to offset all the investment under only one application. Even if the app is successful, it will demand much more time to return the investment.
BaaS x MBaaS
BaaS and MBaaS are pretty much the same things! You can use a backend as a service for web projects or mobile projects. It’s recognized as a mobile backend as a service (MBaas) if it’s used for mobile development.
Why use a backend as a service?
A BaaS platform will help you to solve two problems:
- Manage and scale cloud infrastructure
- Speed up backend development
The reasons to use a backend as a service platform can be broken down into business and technical aspects.
Business reasons to use a BaaS
The business advantages of a backend as a service are mainly related to productivity gains and outsourcing cloud management responsibilities. In particular, for a small to medium size projects, you will have substantial benefits using a backend platform. The math is pretty simple, a backend/infrastructure engineer will cost around $80k/year in the USA. Outsourcing part of the work to a third party will allow offsetting this cost. The other advantage is delivering faster time to market to a software project. Waiting for several months to provide a software product may kill the market opportunity or at least make you start behind the competition.
So, the business advantages of a BaaS are:
- Reduce time to market
- Save money and decrease the cost of development
- Assign fewer backend developers to a project (same results with fewer developers)
- Outsource cloud infrastructure management
Technical reasons to use a BaaS
Good backend developers are difficult to find and are well-paid professionals. So, if you find one of them, make sure you use their time wisely and ask them to deliver high-value code. Programming, repetitive activities, and boilerplate code is a waste of time and money. So, it has to be avoided. The other advantage of a backend service is that it will let your frontend developers concentrate on what they are best at. That is, delivering frontend code and excellent usability for your application.
So, the technical advantages of a BaaS are:
- Focus on frontend development
- Excludes redundant stack setup
- No need to program boilerplate code
- Standardize the coding environment
- Let backend developers program high-value lines of code
- Provides ready to use features like authentication, data storage, and search
- Let you clone apps and run testing environments
- Has ready to use security settings and backup procedures
When to use a backend as a service?
Here are three everyday use cases for using a backend as a service platform:
- Making an MVP — Minimum Viable Product
- Stand-alone apps or applications that require a small number of integrations
- Enterprise apps that are not mission-critical
For these cases, using a BaaS is a no-brain and will save you a lot of money and time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a BaaS
Here are the pros and cons of using a backend as a service.
Advantages of a Backend as a Service
- Development speed — It’s super fast
- Development price — It’s really cheap
- It’s serverless, and you don’t need to manage infrastructure
Disadvantages of a Backend as a Service
- Less flexibility in comparison to custom coding
- A lower level of customization in comparison to a custom backend
- Vendor lock-in for closed source platforms
BaaS x AWS x Azure x Google Cloud
I will explain here, in a straightforward way, the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and BaaS.
First, the definitions.
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service — Examples are AWS, Google Cloud, Azure
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service — Examples are Heroku, Engine Yard
BaaS stands for Backend as a Service — Examples are Back4App, Parse, Firebase
Every time you move from IaaS to PaaS and from PaaS to BaaS, you add layers of service (or layers of value) to your application.
Here is a simple overview:
IAAS = Data Center + Servers + Storage +Networking
PAAS = IAAS + Deploy + Manage + Scale
BAAS = PAAS + Features to Build Backend
IaaS vs PaaS x BaaS
A backend as a service will provide you with features that can be deployed across applications of all types. Here are the most common features of a backend as a service.
- Data Management
- User authentication
- Social Integration (Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, etc.)
- Email Verification
- Push Notifications
- Cloud Code Functions
- Geolocation
- Push Notifications
- CDN and Cache
- Infrastructure (Security settings, auto-scaling, data backup, DB optimization)
Who should use a backend as a service?
A BaaS platform is a technical service and designed for developers. A user with no specialized skills will face challenges in using it. The most common uses cases are:
- Frontend engineers with limited knowledge in backend development
- Backend engineers that want to speed up development
- Engineers that wish to outsource low value/repetitive tasks to a third party
How does a BaaS architecture look like?
Generally speaking, a backend as a service is divided into three different layers. The first layer is the foundation and contains the database servers. A database cluster will have at least two servers to replicate data and a backup routine to allow data to be retrieved. The second layer is the application cluster and contains multiple servers to process requests. The quantity of servers fluctuates throughout the time of the day, and auto-scaling procedures are necessary to fulfill the group with the correct amount of servers. The third layer connects the application servers to the Internet, and it’s composed of load balancers and CDNs.
Backend as a service companies
Here is a comprehensive list of BaaS and mBaaS providers.
1. Back4App
Considering I invested a lot of time writing this article and it is 11:08 PM now, I will start with Back4App, which is the company I work for. Please try it first. You will like it so much that you will not need to try the other platforms and it will save you time. If you don’t like it, please email me at [email protected] and say the reasons.
Our product has the following features: database management, live queries (realtime database), graphQL, push notifications, social login, SDK integration, user management, geo queries, CDN, cache, and several others.
The technology stack it’s based on open source technology. Our stack covers Parse Server, MongoDB or Postgrees and NodeJS. On top of the open-source, we have a set of implementations that improve general performance and dashboards that make the platform more comfortable to use. It’s like hosting Word Press by yourself versus hosting with a professional hosting service.
Another important aspect of our platform is that we take care of scaling. We have some pretty large apps running with us, and a well-designed architecture is instrumental in delivering performance and reliability.
There is a limited free tier available and paid plans to start at $5/mo. The free level is designed for development purposes, and production applications usually run a paid plan.
The advantages of using Back4App are the following:
Easy of use: The platform is really simple to use and takes no more than five minutes to start coding a simple app.
Flexibility: You can manage your open-source code versions, and the source code can be adapted if necessary for best performance.
Hosting: Several hosting options available and service is very reliable. It offers a fully serverless structure or dedicated instances to the customers that demand so.
CDN — Content Delivery Network: The apps hosted at Back4App will automatically distribute content globally. All regions, except for China (we are working on it and have it available soon).
GraphQL: This a new implementation and will provide the most advanced query language for your API. The benefits are retrieving data in a single request and in a predictable way.
Support: 24/7 support. Different support levels are available according to the budget of each client.
2. Parse
It’s an open-source framework supported by a large community of developers. It has more than 30k stars and 15 forks on Github. The goal of Parse is to provide developers a way to create apps faster, and the framework will do that providing developers a stack that covers an API server module for Node.JS, a dashboard to manage apps, SDK & Libraries, adapters and documentation.
This technology used to be hosted by Facebook, but they decided to provide no longer hosting services in 2017. So, you need to self-host the framework or use specialized hosting services. Alternatives to self-host Parse are the leading cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Digital Ocean. The open-source framework is entirely free, and the only cost you will incur is hosting the framework.
The advantages of using the Parse framework are the following:
Data Management: It’s possible to store essential data types, queries, locations, pictures with just a few lines of code. Parse allows you to handle, search, filter, and update your content with a web-based data browser.
Simplicity: The framework is straightforward, and the learning curve will take less than one hour for small projects.
Flexibility: Working with an open-source framework takes versatility to the next level. You can adapt the source code and adjust for your specific needs.
Custom Code: Parse will provide you with a feature called Cloud Code. You will be able to custom code using Javascript with this feature.
Multiplatform: There is plenty of SDKs available, and you can use Parse in almost every platform. It handles mobile, web, and IoT technologies.
GraphQL: Delivers the most advanced query language for your API. The advantages are recovering data in a single call and in a predictable way.
3. Firebase
It’s a closed-source platform that was acquired by Google in 2014, and the backend service assists to quickly produce applications. Firebase covers features like analytics, authentication, real-time database, and hosting. There is a limited free tier available and paid plans to start at $25/mo.
Google started to invest heavily on Firebase in 2016, and the strategy covers three main pillars:
Development Features: This block cover tools to accelerate mobile app development and includes user authentication, storage, real-time database, machine learning, and cloud functions. Cloud Firestore lets you sync data across multiple devices, query, structure data with collections/documents, and sync online/offline data.
Analytics Services: Firebase will provide a comprehensive set of mobile analytics services that will help you to improve general app performance. These services include performance monitoring, Google Analytics, crash reports, and a test laboratory to run automated tests.
Growth: Firebase integrates with a service called Ad Mob that will let you run in-app advertisements. The other growth tools Firebase provides are A/B testing, messaging, and dynamic links.
The advantages of using Firebase are the following:
Realtime database: This feature will allow creating, for example, messaging apps like WhatsApp that will update data across devices almost instantly.
Machine Learning: This is a cool feature available in Firebase and not available in other backends as a service platform. It will provide a set of ready to use API with standard machine learning use cases like face recognition, scanning, and recognizing texts.
Ad Mob: This feature will allow you to monetize your app and integrate it into a global ad network managed by Google.
4. Cloudkit
It’s a closed-source backend platform that is run by Apple and used to develop iOS applications and has native SDK for it. The service is available since 2015, and it’s easy to integrate with iOS apps. The structure provides database, auth, file storage services letting developers concentrate on client-side development. CloudKit is primarily a data store with essential iCloud identification authentication support and an API in front of it. It has fewer features in comparison to other services listed here. Pricing increases pretty fast and costs $100 for every ten req/s.
The main advantage of using CloudKit is the native SDK for iOS. Native applications run on the iPhone operating system and have complete access to the device and functionally. So, it will lead to the best performance possible, user experience, and design.
5. Kinvey
It’s an enterprise-focused backend as a service and Progress Software acquired Kinvey in 2017. Allow you to operate enterprise apps using a serverless design, and the features are similar to other backend providers. It covers database, authentication, push notifications, and location services. All plans include hosting and operation. The free version is limited to 100 users, and the pricing is pretty expensive, and the enterprise version starts at $24,000/year
The advantages of using Kinvey are the following:
Popular Enterprise Integrations: As I mentioned, this backend platform is suited for enterprises. The service covers integrations like Salesforce, SAP, Workday, Microsoft Active Directory, and Oracle.
Operational Intelligence Tools: Compliance and analytics reports. It provides HIPAA compliant apps for healthcare
Support: 24/7 available.
6. Backendless
They are one of the first players in this market and are running the platform for a long time without venture funding. This vendor provides two types of hosting. You can use the online service or run the framework locally. There is a limited free tier for online hosting and paid plans to start at $15/mo.
The advantages of using Backendless are the following:
Standalone Version: You can run this version locally on your server or in any cloud platform.
Cache Feature: This feature is convenient and available in standalone and cloud hosting.
Support: They provide 24/7 support to the users.
7. AWS Amplify (previous AWS mobile hub)
It’s an open-source library that works together with Amazon Web Services. It supports developers to create scalable serverless applications and smoothly integrates with iOS, Android, React Native, and web frontends. The features available cover Analytics, Notifications, AR/VR, storage, and APIs. The service has a small free tier and a Pay as you Go plan for production environments.
The advantages of using AWS Amplify are the following:
CDN — Content Delivery Network: It’s super easy to integrate with CloudFront and deploy content globally.
GraphQL: Amplify provides a feature called GraphQL Transform that makes it easier for the process of developing.
Atomic Deployments: This feature will allow your app to keep working even if the construction process crashes on new releases.
8. Azure Mobile Apps
Microsoft could not be out of this game and also has a backend as a service solution. The backend platform integrates with Xaramim (frontend cross-platform) and Azure.
The advantages of using Azure Mobile Apps are the following:
Security Protocols: Microsoft provides enterprise-level security to create apps, and they are good at it.
Off-Line Sync: This feature is handy and allows users to sync data automatically.
AD Integrations: This is another enterprise feature that will allow corporate sign-on.
It’s a backend development platform for games, IoT, and apps in general. It works in public, private, and local clouds. The features contain push notifications, data and user management, A/B testing, geolocation, and analytics.
9. Kii
The advantages of using Kii are the following:
Multiple deployment options: You can run the solution in any cloud and on premisses.
IoT: The platform has ready to use features for IoT interactions.
Niche Solutions: They have specific solutions for Agriculture, Asset Management, Beacons, etc.
10. Kumulos
It is a backend platform created for mobile app development companies and mobile digital agencies. It helps these companies to develop applications for their customers. The feature list includes push notifications, reporting and analytics, and app store optimization. It has 3 pricing tiers covering Startups, Digital Agencies, and Enterprises.
The advantages of using Kumulos are the following:
Crash Reports & Diagnostics: Helps developers to find issues faster and take action to solve.
App Store Optimization: This is a unique feature among all backend as service companies and only available in Kumulos.
Agency Console: This is convenient and allows a software development company to manage multiple apps under a corporate account.
Other BaaS Platforms
Below you can see a list with some other backend providers.
- Game Sparks (backend for games)
- Playfab (backend for games)
- Appcelerator
- MongoDB Stich
- Oracle Mobile Hub
- IBM Mobile Foundation
- Baqend
- Convertigo
- BaasBox
- Kuzzle
- Hoodie (self-hosted backend)
Conclusion
Applications have a frontend, a backend, and APIs connecting both sides. A backend as a service or Baas (mBaaS for mobile apps) will help you to automate part of the work of developing backend code. The backend service providers will also have the responsibility to deploy, manage, and scale applications. The main reasons to use the backend as a service platforms are the reduction of time to launch an app, lower development costs, and outsourcing infrastructure management. The most common features of a BaaS are data modeling, user authentication, social integration, push notifications, and others. The leading players of the market include Back4App, Parse, and Firebase.
So, what do you think about the results we accomplished? Has it helped you figure out what a backend as a service is?
If you would like to add information to this tutorial, contact me at george@back4app.com, and I will be glad to enter your observations.
Would you like to know more? Please read these other articles:
What is a backend as a service
New approach to backend as a service market
What is a Backend as a Service
O que e um Backend as a Service
Originally published at blog.back4app.com on July 24, 2019.